Deploy Your Backend Securely and Effortlessly with Vercel
Why Deploy Your Backend on Vercel? When you're working on a personal project that needs a backend (server-side code). Vercel enforces HTTPS for your backend. This ensures safe communication between your front end and back end. This is critical. Browsers block mixed content (HTTP within HTTPS pages) to stop security holes. Deploying on Vercel lets you avoid this browser restriction. It also guarantees a secure user experience. This makes it a budget-friendly solution for deploying backend code. This allows you to experiment and build without worrying about upfront costs. Getting Started with Vercel Deployment Here's a guide to deploying your backend on Vercel. This works even if you're using a MongoDB as your backend storage. Project Setup Create a new directory for your project. mkdir deployvercel Initialize a Node.js project using yarn init or npm init. Install Express.js yarn add express or npm install express Create a file named index.js and define your backend logic within this file. This includes setting up Express routes. It means defining API endpoints and handling database interactions (if needed). Run the Application Locally Add a script to your package.json file to run your backend application locally: JSON scripts": { "dev": "nodemon index.js", } To start the backend server Run npm run dev or yarn dev Configure Vercel Deployment (vercel.json) Put a vercel.json file in your project's root directory. It tells Vercel how to handle your backend code. Here is the configuration: { "version": 2, "builds": [ { "src": "index.js", "use": "@vercel/node" } ], "routes": [ { "src": "/(.*)", "dest": "index.js", "methods": ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE", "OPTIONS"] } ] } This configuration tells Vercel to use its Node.js build process. It handles all requests to your backend using the index.js file. Deploy to Vercel Using Git Push your code to GitHub. In your Vercel dashboard, add a new project and connect it to your Git repository. Vercel will find your vercel.json file. It will deploy your backend when you push code changes to your Git repository. With these steps, you'll have a secure backend. It will be scalable and globally distributed. It will be deployed on Vercel and ready to serve your frontend or API. Github Url https://github.com/Amity808/deployVercel-tutorial
Why Deploy Your Backend on Vercel?
When you're working on a personal project that needs a backend (server-side code).
Vercel enforces HTTPS for your backend. This ensures safe communication between your front end and back end. This is critical. Browsers block mixed content (HTTP within HTTPS pages) to stop security holes. Deploying on Vercel lets you avoid this browser restriction. It also guarantees a secure user experience.
This makes it a budget-friendly solution for deploying backend code. This allows you to experiment and build without worrying about upfront costs.
Getting Started with Vercel Deployment
Here's a guide to deploying your backend on Vercel. This works even if you're using a MongoDB as your backend storage.
Project Setup
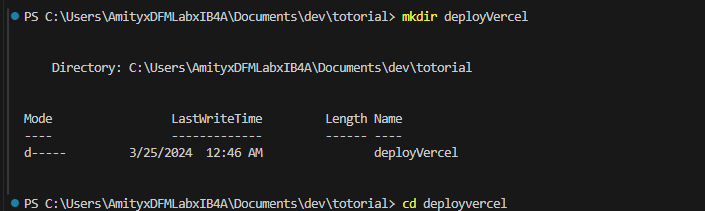
Create a new directory for your project.
mkdir deployvercel
Initialize a Node.js project using yarn init or npm init.
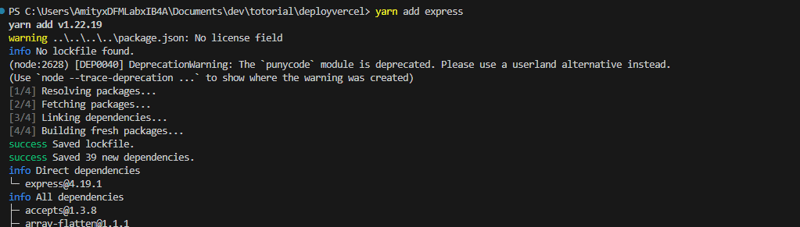
Install Express.js
yarn add express
or
npm install express
Create a file named index.js and define your backend logic within this file. This includes setting up Express routes. It means defining API endpoints and handling database interactions (if needed).
Run the Application Locally
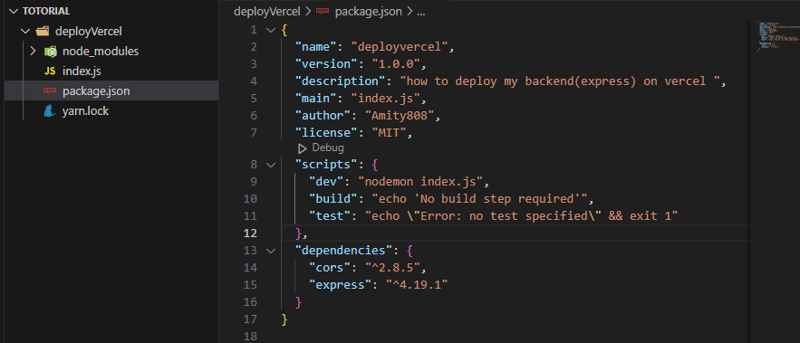
Add a script to your package.json file to run your backend application locally:
JSON
scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon index.js",
}
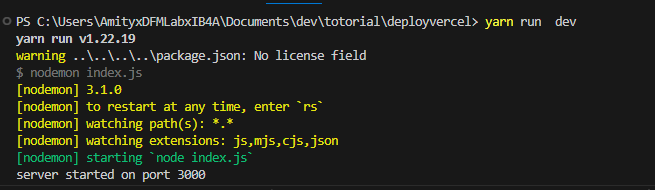
To start the backend server Run
npm run dev or yarn dev
Configure Vercel Deployment (vercel.json)
Put a vercel.json file in your project's root directory. It tells Vercel how to handle your backend code. Here is the configuration:
{
"version": 2,
"builds": [
{
"src": "index.js",
"use": "@vercel/node"
}
],
"routes": [
{
"src": "/(.*)",
"dest": "index.js",
"methods": ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE", "OPTIONS"]
}
]
}
This configuration tells Vercel to use its Node.js build process. It handles all requests to your backend using the index.js file.
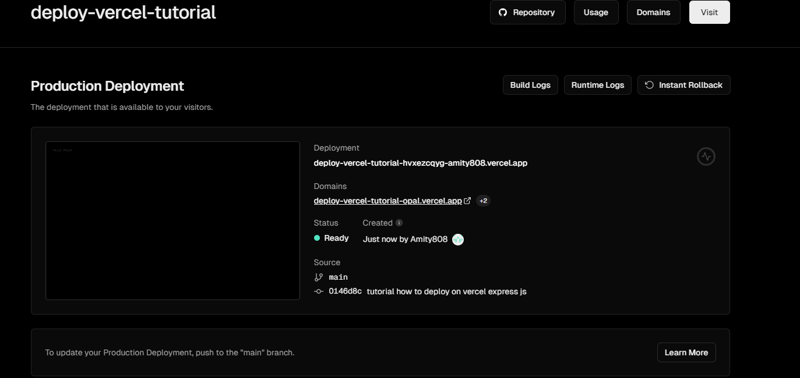
Deploy to Vercel Using Git
Push your code to GitHub.
In your Vercel dashboard, add a new project and connect it to your Git repository.
Vercel will find your vercel.json file. It will deploy your backend when you push code changes to your Git repository.
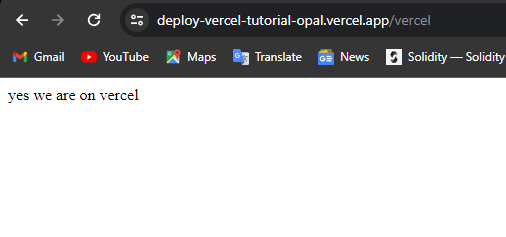
With these steps, you'll have a secure backend. It will be scalable and globally distributed. It will be deployed on Vercel and ready to serve your frontend or API.
Github Url
https://github.com/Amity808/deployVercel-tutorial
What's Your Reaction?